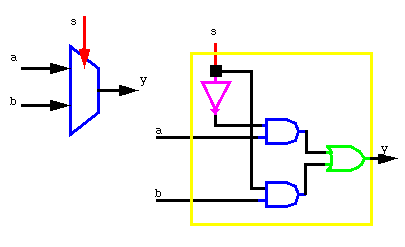
![]() a multiplexer
selects one of two or more signals and passes it to the output.
a multiplexer
selects one of two or more signals and passes it to the output.
use of selected signal and if statements
use of case and select statements
| library IEEE;
use IEEE.std_logic_1164.all; entity mux_2to1 is port(a,b,s: in std_logic;y: out std_logic); end mux_2to1; |
| architecture
data_flow_1 of
mux_2to1 is
begin y <= a when s='1' else b; -- select signal assignment end data_flow_1; |
| architecture
process_1 of
mux_2to1 is
begin process(a,b,s) -- s selection signal ; full list begin y <= b ; -- default assignment if (s ='1') then y <= a; end if; end process; end process_1; |
| architecture
process_2 of
mux_2to1 is
begin process(a,b,s) -- s selection signal ; full list begin if (s ='1') then y <= a; else y <= b ; end if; end process; end process_2; |
![]() four-bit
wide 4-1 multiplexer:
four-bit
wide 4-1 multiplexer:
| library IEEE;
use IEEE.std_logic_1164.all; use IEEE.numeric_std.all; entity mux_4to1 is port(s: unsigned(1 downto 0);a,b,c,d: in unsigned(3 downto 0); y: out unsigned(3 downto 0)); end mux_4to1; |
| architecture
data_flow of
mux_4to1 is
begin with s select -- selected signal is concurrent statement y <= a when "00", y <= b when "01", y <= c when "10", y <= d when "11", d when others; end data_flow; |
| architecture
process_mux of
mux_4to1 is
begin process(a,b,c,d,s) -- s selection signal ; full list begin case s is when "00" => y <= a; when "01" => y <= b; when "10" => y <= c; when "11" => y <= d; when others => y <= d; end case; end process; end process_mux; |